Return the relative position of a specified item in a range
=XMATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_mode], [search_mode])
XMATCH is a modern and more flexible replacement for the MATCH function. XMATCH works in any direction, supports wildcards (* ?) for partial matches and returns exact matches by default. XMATCH can search from the first or last value in a list like XLOOKUP.
XMATCH is only available to Excel 365 subscribers.
XMATCH returns the relative position of a specified item in a range. It defines 'what to match', 'where to search', 'the match type to return' and 'whether to search from the first or last value'.
Use XMATCH to find the position of a value in a range instead of the value itself (e.g. in the row_num argument of the INDEX function.
XMATCH and text values
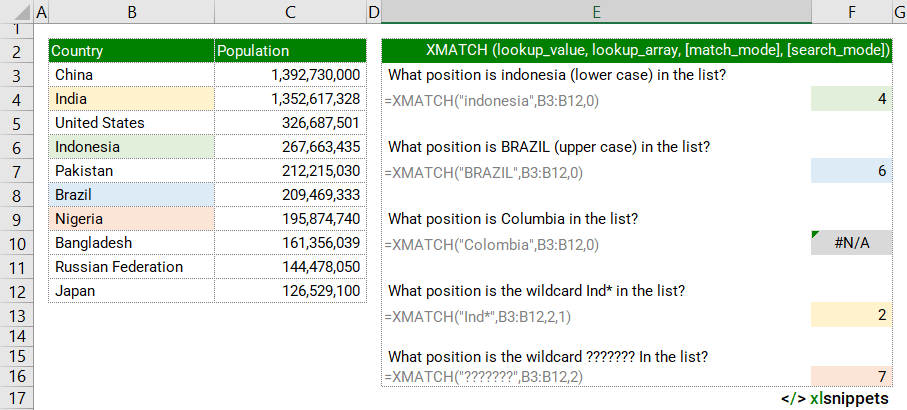
In the examples below, the XMATCH function is used to match country names to a list. The lookup_values are case insensitive. #N/A is returned for values not found in the list and wildcards (* ?) are accepted with the match_mode set to 2.
Use the XMATCH function to return the relative position of a specified item in a range.
XMATCH and numerical values
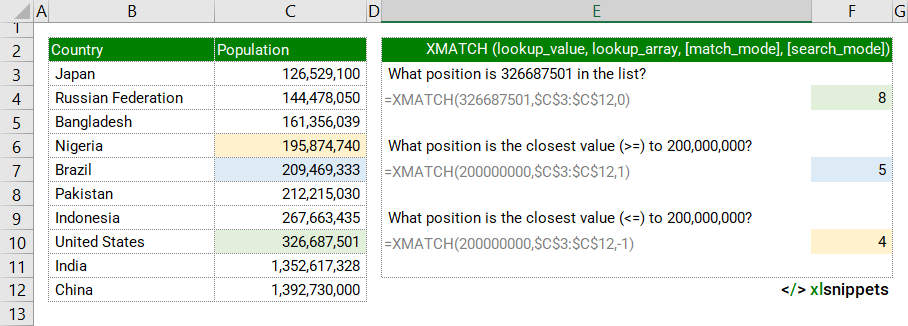
In the examples below, the XMATCH function is used to match country populations to a list in ascending order. A match_mode of 0 returns exact matches. -1 returns an exact match or next smallest value. 1 returns an exact match or the next largest value.
Use the XMATCH function to return the relative position of a specified number in a range.
Syntax
=XMATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_mode], [search_mode])
The XMATCH function consists of at least 2 arguments out of 4:
- lookup_value. Required. The value to be matched.
- lookup_array. Required. A range of cells to be searched.
- match_mode. Optional. -1, 0, 1 or 2.
- -1 finds the exact match or the next smallest value that is less than or equal to the lookup_value.
- 0 (default) finds the first value that is an exact match to the lookup_value.
- 1 finds the exact match or the next largest value that is greater than or equal to the lookup_value.
- 2 enables wildcards (* ?) to be used in the lookup_value.
- search_mode. Optional. 1, -1 , 2 or -2.
- 1 (default) searches first-to-last.
- -1 searches last-to-first.
- 2 runs a binary search that requires lookup_array to be in ascending order. Invalid results are returned if lookup_array is not sorted.
- -2 runs a binary search that requires lookup_array to be in descending order. Invalid results are returned if lookup_array is not sorted.
Try it now!
- Enter your formulas into the grey cells.
Scope
XMATCH defines 'what to match', 'where to search', 'the match type to return' and 'whether to search from the first or last value'.
|
=XMATCH("indonesia",B3:B12,0) || result is the position of the lookup_value "indonesia" in the lookup_array B3:B12. MATCH is case insensitive, not distinguishing between upper and lowercase letters. |
|
=XMATCH(326687501,$C$3:$C$12,0) || result is the position of the lookup_value 326,687,501 in the lookup_array C3:C12. The #N/A error value is returned if no exact match (based on the optional match_mode) is found. |
|
=XMATCH(200000000,$C$3:$C$12,1) || result is the next value from the lookup_array C3:C12 that is greater than or equal to the lookup_value 200,000,000. |
|
=XMATCH(200000000,$C$3:$C$12,-1) || result is the next value from the lookup_array C3:C12 that is less than or equal to the lookup_value 200,000,000. |
|
=XMATCH(5,{6,5,4,3,2,1}) || result is 2, as 5 is the second value in the array. =XMATCH(4.5,{6,5,4,3,2,1},-1) meanwhile would return 3 as the match_mode argument is set to 1, returning an exact match or the next smallest value which is the number 4 in position 3 in the array. |
Caveats
- XMATCH returns the position of the matched value, not the actual value itself.
- XMATCH can be combined with the INDEX function to retrieve a value from a specific matched position. XMATCH identifies the position of the value and INDEX returns the value at that position.
- lookup_value
- Can be a number, text, logical value or cell reference. Text strings can be up to 255 characters in length.
- XMATCH does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase.
- Wildcards (* ?) can be used in text strings. To find actual question marks (?) or asterisks (*), place a tilde (~) before the character.
- match_mode
- match_mode is optional and defaults to 0 (exact match).
- XMATCH returns the #N/A error if no match can be found. Use the IFNA function to trap and handle #N/A errors.
- search_mode
- search_mode is optional and defaults to 1 (search first-to-last).
- Binary searches are very fast but require data to be sorted in the correct order.
Common issues
- #N/A: lookup_value can not be matched in the lookup_array.
Related Functions
Functions Category



