Sum (add) values in a range that meet a single criteria.
SUMIF(range,criteria,[sum range])
SUMIF (without the 's'!) allows you to add up values associated with one set of specific criteria in a range or table.
The SUMIF syntax requires the range to be searched, the criteria to look for and the range of values to sum (add) up.
SUMIF can be used with dates, numbers, and text and supports logical operators (>,<,<>,=) and wildcards (*,?) for partial matching.
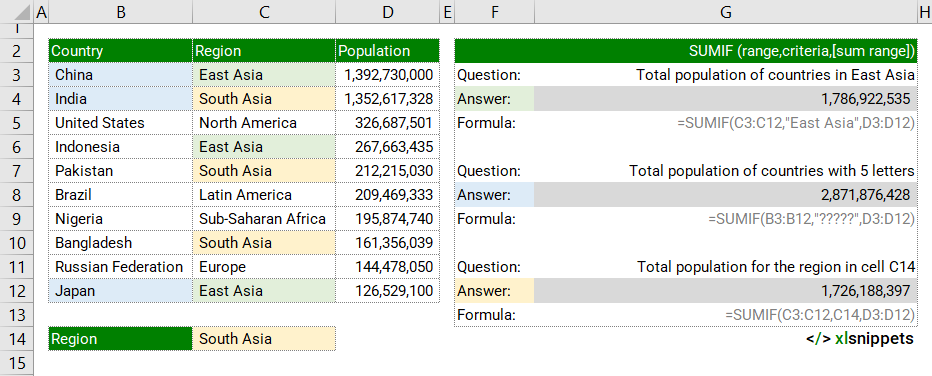
SUMIF and text.
In the examples below, the data range shows a list of countries, the region they belong to and their respective population. SUMIF is used to determine total population for countries in specific regions or with a certain amount of letters in their country name.
Use the SUMIF function to add values in a range that meet a single criteria.
Note: SUMIF works slightly differently to the SUMIFS (with the 's'!) function which allows you to add up values associated with multiple criteria. For example, with a SUMIFS function, you could determine total population for a specific region excluding a certain country. This would not be possible with the SUMIF function which only permits one criteria. The SUMIFS function uses a slightly different syntax so instead of learning both, just use the SUMIFS function which can be used with one or multiple criteria.
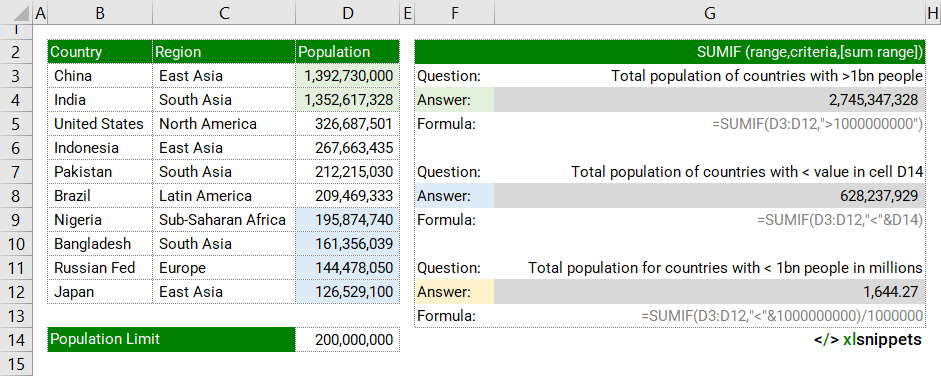
SUMIF and numbers.
In the examples below, SUMIF is used to determine the total population of all countries where their own population is greater or less than specific values (either stated or referenced from another cell). Note that the logical operators (<>) are included in quotations with stated values (e.g. (">200000000") but are concatenated with cell references (e.g. "<" & C14). Note that the optional sum_range is not included; the cells in the range are summed instead.
Use the SUMIF function to add values in a range that meet a single criteria using a concatenation and cell reference.
SUMIF and dates.
In the examples below, SUMIF is used to determine total sales for given dates or date ranges. Dates can be expressed as stated values ("1-Mar-22") or as cell references or using the DATE function (=DATE(2022,3,1)).
Use the SUMIF function to add values in a range that meet a single criteria using a date reference.

Syntax
The SUMIF function consists of 3 arguments: =SUMIF(range,criteria,[sum range])
- range. Required. The range of cells to be evaluated by the criteria.
- criteria. Required. The criteria used to evaluate the range.
- [sum_range]. Optional. The range of cells containing the values to sum.
- If sum_range is omitted, the cells in the range are added together instead.
- sum_range should be the same size and shape as range (e.g. C3:C13 and D3:D13). You'll get an error if you use different ranges (e.g. C3:C13 and D3:D18).
Try it now!
- Enter your formulas into the grey cells.
Scope
SUMIF can be applied to ranges, named ranges and tables. It can also be used with logical conditions, wildcards and cell references.
|
=SUMIF(C3:C13,"South Asia",D3:D13) |
|
=SUMIF(Region,"South Asia",Population) |
|
=SUMIF(Table1[Region],"South Asia",Table1[Population]) |
|
=SUMIF(C3:C13,"<>South Asia",D3:D13) // not equal to "South Asia" |
|
=SUMIF(C3:C13,"*Asia",D3:D13) // ends with "Asia" |
|
=SUMIF(C3:C13,"?????",D3:D13) // contains 5 characters |
|
=SUMIF(C3:C13,"<>"&A2,D3:D13) // not equal to value of cell A2 |
Caveats
SUMIF function:
- returns incorrect results when used to match strings longer than 255 characters.
- returns incorrect results when used to match the #VALUE! string.
- is not case sensitive.
- use the * and ? characters for wildcards. To find an actual question mark or asterisk, type a tilde (~) preceding the character.
- range and sum_range should be the same size.
- logical operators (<,>,<>,=) can be used for partial matches and should be enclosed in double quotation marks "" along with non-numeric criteria being evaluated (quotation marks are not required for numeric values).
- cell references in criteria are not enclosed in quotes, i.e. "<"&A1
Related Functions
- SUMIFS: sum (add) values in a range that meet specific or multiple criteria.
- COUNTIF count values within a range that meet one specific criteria.
- COUNTIFS count values within a range that meet specific or multiple criteria.
Functions Category



