Returns the arithmetic mean or average of a data set.
=AVERAGE(number1, [number2], ...)
Return the the arithmetic mean or average of a set of numbers using either defined values (e.g. 1,1,2,3) or ranges, named ranges, arrays or cell references (e.g. C3:C6). The AVERAGE function can also handle a mix of constants and references (e.g. 1,C1,C2,4)
AVERAGE syntax requires the number arguments to be considered. The function adds the numbers together and divides by the total number of values supplied. A similar result can be achieved using the SUM and COUNT functions.
AVERAGE with a number.
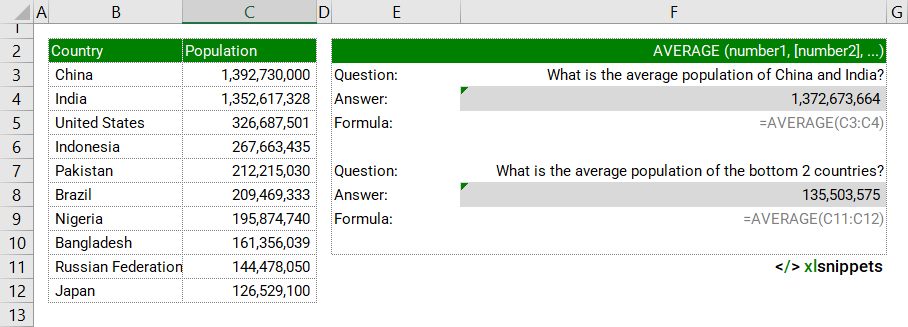
In the example below, the AVERAGE function is used to identify the arithmetic mean or average of country populations using cell ranges.
Use the AVERAGE function to return the arithmetic mean or average of a data set.
Syntax
=AVERAGE (number1, [number2], ...)
The AVERAGE function consists of at least 1 argument:
- number 1. Required. A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
- number 2. Optional. A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
Try it now!
- Enter your formulas into the grey cells.
Scope
AVERAGE can be applied to numbers, ranges, named ranges, arrays or cell references. Up to 255 numbers can be used as separate arguments.
|
=AVERAGE(1,2,3,4,5) || result is 3 |
|
=AVERAGE(C3:C10) where the range holds values in each cell. |
Caveats
- The AVERAGE function will include zero values when calculating an average.
- To exclude zero values, or other values based on logical criteria, use the AVERAGEIF or AVERAGEIFS functions.
- Arguments can be numbers, defined names, arrays, or cell references that contain numbers.
- Empty cells, and cells that contain boolean values or text will be ignored by the AVERAGE function. To include these values in a calculation, use the AVERAGEA function.
- AVERAGE will return #N/A if there are error values or text that can not be interpreted as a number in the arguments.
Related Functions
- MEDIAN() returns the median or middle number in a data set.
- MODE.MULT() returns the most common values in a data set as an array.
- MODE.SNGL() returns the most common value in a data set.
- MODE() returns the most common value in a data set. Use MODE.SNGL instead.
Functions Category



