Returns the median or middle number in a data set.
=MEDIAN(number1, [number2], ...)
Return the median or number in the middle of a set of numbers using either defined values (e.g. 1,1,2,3) or ranges, named ranges or cell references (e.g. C3:C6).
MEDIAN syntax requires the number arguments to be considered.
MEDIAN with a number.
In the example below, the MEDIAN function is used to identify the median or middle number in a list of defined values or a cell range.
Use the MEDIAN function to return the median or middle value in a data set.
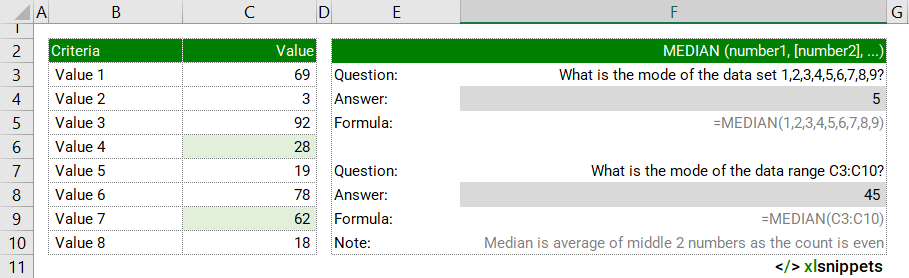
Syntax
=MEDIAN(number1, [number2], ...)
The MEDIAN function consists of at least 1 argument:
- number 1. Required. A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
- number 2. Optional. A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
Try it now!
- Enter your formulas into the grey cells.
Scope
MEDIAN can be applied to numbers, ranges, named ranges or cell references. Up to 255 numbers can be used as separate arguments.
|
=MEDIAN(1,2,3,4,5) || result is 3 |
|
=MEDIAN(C3:C10) where the range holds values in each cell. |
Caveats
- If there is an odd number of values, the middle number is returned.
- If there is an even number of values, the median is calculated as the average of the two numbers in the middle.
- Arguments can be numbers, defined names, arrays, or cell references that contain numbers.
- Empty cells, and cells that contain boolean values or text will be ignored by the MEDIAN function. Cells with the value zero (0) will be included.
- MEDIAN will return #N/A if there are error values or text that can not be interpreted as a number in the arguments.
Related Functions
- AVERAGE() returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the values in a data set.
- MODE.MULT() returns the most common values in a data set as an array.
- MODE.SNGL() returns the most common value in a data set.
- MODE() returns the most common value in a data set. Use MOMODE.SNGL instead.
Functions Category



